We are on a mission to Create Website for every Business in India and across the Globe.
Domain Services
In Domain-Driven Design (DDD), a domain service is a component that encapsulates a specific business rule or operation that is not naturally a part of an entity or value object. A domain service defines a set of methods that perform operations that are specific to the domain and that do not fit into any of the existing domain objects.
For example, a banking application might have a domain service that handles the transfer of funds between accounts. This operation involves multiple domain objects (e.g. accounts) and may also have complex business rules (e.g. validating that the accounts involved in the transfer belong to the same customer), so it’s not something that can be handled by a single entity or value object. In this case, a domain service would be the appropriate place to encapsulate this behavior.
A domain service should be used only when it makes sense in the context of the domain, it should be stateless, and it should have no persistence of its own.
It is important to note that a domain service is not a technical service, it is a Domain-specific service, it should be used to solve a specific business problem, and it should be named after the business concept it represents.
In addition to domain services, there are several other types of services that can be created when working with Domain-Driven Design (DDD):
- Application Services: These services handle the presentation and coordination of the application. They handle the input and output of the system and act as an intermediary between the application’s user interface and the domain model.
- Infrastructure Services: These services handle the technical aspects of the application such as persistence, logging, and communication. They provide the necessary functionality for the application to run, but they should not contain any domain logic.
- Interface Adapters: These services handle the conversion of data between the domain model and external systems such as a database or a web service. They are responsible for mapping data between the different representations of the same information.
- Factories and Repositories: These services handle the creation and retrieval of domain objects. Factories are responsible for creating new objects and initializing them with the appropriate data, while repositories are responsible for retrieving existing objects from the persistence layer.
It is important to note that all of these services should be organized in such a way
Features of Company Website Designing Services
We are the core website design company with team of company web designers as per client requirements.
- Creative website
- Fast Loading website Speed
- Free website Maintenance
- Low Cost web design
Service Domains and Domain Categories
Service Domains are logical groupings of service-level aspects that enable the system to measure provisioning in different categories. Examples of Service Domains include Availability, Backup, and Help Desk. Service Domains have Domain Categories that describe the specific aspects of common service-level characteristics. You can create as many Domain Categories as needed for your customer service agreement. You can create specific Domain Categories to define Metrics to use in Contracts. Domain categories enable the user to view specific measurements of selected service aspects.
- Responsive website design
- Quick Delivery
- Yearly website maintenance services
- SSL Certificate
Add a Service Domain
- Click Design, Foundation Entities, Service Domains.
- Click Add New.
- Specify a name and description.
Click Save&Continue.
CA Business Service Insights adds the service domain to the system.
Domain Categories
Add a Domain Category
- On the Service Domains page, click
next to the Service Domain.
- Click Add Domain Category, and specify the Name and Description.
- Select the maximum or minimum target for the service level from the Default Service Level Target drop-down list. For example, “Mean Time to Repair takes a maximum 6 hours” or “Service Availability is a minimum of 99%”.
- In Report precision, specify the number of decimal places to display in reports.
- Select a unit of measurement for all the metrics for this domain category from the drop-down list.
- (Optional) Specify the minimum or maximum value for the service-level target, according to the unit of measurement.
(Optional) To specify that the calculation engine creates best-case and worst-case scenarios for this domain category, select Prediction metric.
The system uses the predictions for alerts and dashboard thresholds. The predictions are based on the results for the tracking period up to the date of the calculation.The following steps relate to predictions:
If you selected Prediction metric, select a function from the Prediction metric drop-down list. The prediction uses the selected function to produce scenarios, as follows:
- Average (weighted average)
- Maximum
- Minimum
- In Optimistic value and Pessimistic value, specify the best-case and worst-case values.The system uses these values in the calculation of certain alerts, such as Predicted Penalty and Predicted Service Level, and for Dashboard thresholds.
In Thresholds, define threshold values for roll-up calculations in the Dashboard.
- In Thresholds refer to, select if the thresholds are defined as Measurement or Deviation.
- In Threshold values, set a value for the Yellow threshold and the Red threshold for Dashboard calculations.
Click Save.
CA Business Service Insights adds the domain category to the service domain.
Sample Service Domains and Domain Categories
The following table lists common service domains and domain categories:
| Service Domain | Domain Category |
|---|---|
| System Availability | % of time available Number of outages/downtimes Mean time to repair Mean time between failures |
| Service Availability | Minutes of downtime Number of disrupted days Financial Management Service cost |
| Process Performance | % Processes completed on time Number completed process cycles % Incidents resolved < T1 |
| Incident Management | % Incidents responded to < T1 Number of incidents % Incidents converted to problem |
| % Customer satisfaction | Average CSI score |
| Helpdesk Performance | % Abandoned calls Average call pickup time % FLLR (First-Level Resolution Rate) |
| Data Quality | % Accuracy % Timeliness Number of errors/defects |

50% Off Get a Free Proposal
Samridh Sathi Google Map
Explore our services
- Benefits of Business Website
- Startup Website Design
- Landing Page Design
- Website Cost in India
- Website Redesigning Services
- Informative Website Designing
- Dynamic Website Development
- Ecommerce Website Development
- Custom Website Designing
- Laravel Development
- SEO Services
- Social Media Optimization
- Software Development
- Web Portal Development
- Website Maintenance Services
- WordPress Development
- Corporate Website Design
- News Portal Development
- PHP Development Services




Industries we serve
Pan India Web Design Services




Introduction of Active Directory Domain Services
A directory is a hierarchical structure that stores information about objects on the network. A directory, in the most generic sense, is a comprehensive listing of objects. A phone book is a type of directory that stores information about people, businesses, and government organizations. Phone books typically record names, addresses, and phone numbers. Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft technology used to manage computers and other devices on a network. It is a primary feature of Windows Server, an operating system that runs both local and Internet-based servers.
Benefits of Active Directory –
- Hierarchical organizational structure.
- Multimaster Authentication & Multimaster replication (the ability to access and modify AD DS from multiple points of administration)
- A single point of access to network resources.
- Ability to create trust relationships with external networks running previous versions of Active Directory and even Unix.
- It provides a centralized location for managing user and computer accounts, which can save time and increase efficiency for IT administrators. This also allows for consistent application of security policies and permissions.
- It provides a range of security features, including password policies, group policies, and access controls, which can help to protect the network from unauthorized access and malicious activity.
- Designed to support large networks with many users and devices, and can easily scale to meet the needs of growing organizations. This includes the ability to add additional domain controllers and servers as needed.
- Makes it easy to share resources such as files and printers across the network, and to manage access to these resources through permissions and security settings.
- Comprehensive auditing and reporting capabilities, which can help organizations to track changes and activity on the network, and to identify potential security issues.
Directory Service – A directory service is a hierarchical arrangement of objects which are structured in a way that makes access easy. However, functioning as a locator service is not AD’s exclusive purpose. It also helps organizations have a central administration over all the activities carried out in their networks. Essentially a Network Directory Service:
- Provides information about the user objects, computers and services in the network.
- Stores this information in a secure database and provides tools to manage and search the directory.
- Allows to manage the user accounts and resources, apply policies consistently as needed by an organization.
Active Directory provides several different services, which fall under the umbrella of “Active Directory Domain Services, ” or AD DS. These services include:
- Domain Services – Stores centralized data and manages communication between users and domains; includes login authentication and search functionality
- Certificate Services – It generates, manages and shares certificates. A certificate uses encryption to enable a user to exchange information over the internet securely with a public key.
- Lightweight Directory Services – Supports directory-enabled applications using the open (LDAP) protocol.
- Directory Federation Services – Provides single-sign-on (SSO) to authenticate a user in multiple web applications in a single session.
- Rights Management – It controls information rights and management. AD RMS encrypts content, such as email or Word documents, on a server to limit access.
Domain Controllers – A server that is running AD DS is called a domain controller.Domain controllers host and replicate the directory service database inside the forest. The directory service also provides services for managing and authenticating resources in the forest.These servers host essential services in AD DS, including the following: – Kerberos Key Distribution Center (kdc) – NetLogon (Netlogon) – Windows Time (W32time) – Intersite Messaging (IsmServ) Active Directory Objects:
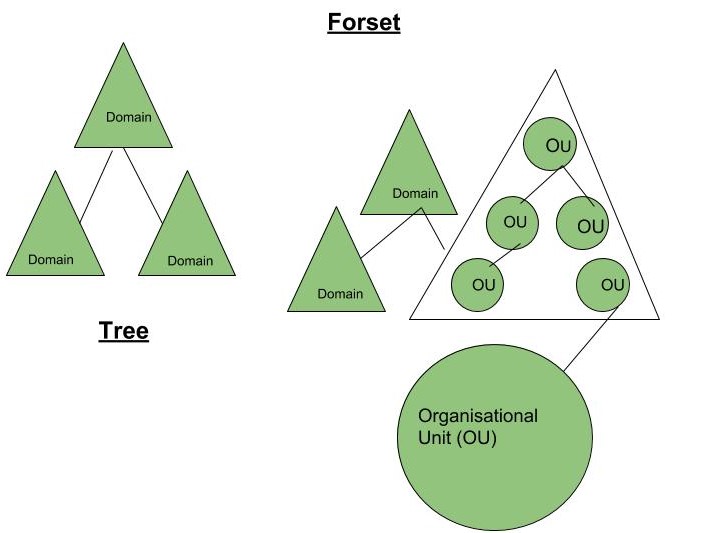
- Container Objects – These objects can contain other objects inside them, and we can make collection from them. For Ex- Forest, Tree, Domains, Organisational Units.
- Leaf Objects – These objects can not contain other objects inside them. For Ex- users, computers, printers, etc.
- Common Terminologies and Active Directory Concepts:
- Schema – A set of rules, the schema, that defines the classes of objects and attributes contained in the directory, the constraints and limits on instances of these objects, and the format of their names.
- Global catalog – A global catalog that contains information about every object in the directory. This allows users and administrators to find directory information regardless of which domain in the directory actually contains the data. For more information about the global catalog, see The role of the global catalog.
- Forest Root Domain – The first domain that is installed in an Active Directory Forest is referred to as the root domain.
- Sites – Sites in AD DS represent the physical structure, or topology, of your network. AD DS uses network topology information, which is stored in the directory as site, subnet, and site link objects, to build the most efficient replication topology.
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol – AD is based on the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). This protocol provides a common language for clients and servers to speak to one another.
- Domain Controller – A domain controller (DC) is a server that contains a writable copy of the Active Directory database and is responsible for authenticating users and computers, as well as enforcing security policies.
- Organizational Unit – An organizational unit (OU) is a container object in Active Directory that can hold other objects, such as users, groups, and computers. OUs are used to help organize objects within a domain and can be used to apply group policies to specific sets of objects.
- Group Policy – Group Policy is a feature in Active Directory that allows administrators to define and enforce policies on groups of computers or users. These policies can include security settings, software deployment, and other system configurations.
- Trust Relationship – A trust relationship is an association between two domains that enables users in one domain to access resources in the other domain. Trust relationships can be one-way or two-way, and can be transitive or non-transitive.
- Replication – Replication is the process by which changes made to the Active Directory database on one domain controller are synchronized with the database on other domain controllers. Replication ensures that all domain controllers have the same information and helps to maintain consistency across the directory.
- Kerberos – Kerberos is a network authentication protocol used by Active Directory to provide secure authentication for users and computers. Kerberos uses encryption to prevent unauthorized access to network resources and is integrated with Active Directory to provide a seamless authentication experience for users.
- Group – A group is a collection of user accounts or computer accounts that can be used to assign permissions or apply policies to multiple objects at once. Groups can be used to simplify administration and improve security by reducing the number of individual permissions or policies that need to be assigned to each object.
Advantages:
Centralized management: AD DS provides centralized management of users, computers, and other network resources, which makes it easier to manage and secure large-scale networks.
Scalability: AD DS can support large-scale networks with tens of thousands of users and devices, making it suitable for enterprise-level organizations.
Group policy management: AD DS provides group policy management, which allows administrators to manage and configure settings for groups of users and computers.
Authentication and authorization: AD DS provides authentication and authorization services, which allows administrators to control access to network resources based on user roles and permissions.
Single sign-on: AD DS supports single sign-on (SSO), which allows users to log in once and access multiple network resources without having to provide credentials multiple times.
Disadvantages:
Complexity: AD DS can be complex to set up and manage, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
Cost: AD DS requires licensing fees and may require additional hardware resources, which can increase the cost of network infrastructure.
Vulnerability: AD DS can be vulnerable to security threats, such as password attacks and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, which can compromise network security.
Compatibility: AD DS is designed for Windows networks and may not be compatible with other operating systems or network environments.
Maintenance: AD DS requires regular maintenance, including software updates and security patches, to ensure optimal performance and security.
Formula's of Domain Services Company
Website Formula
Ready to take your online presence to the next level.

Grow Your Business
Dynamic website ranks high in search engine results.
Expert Team
Our team of experienced designers and developers..
Get a Website Design Package with Web Hosting and Email Ids. Call/WhatsApp :



Trusted by Enterprises across Industries
Our website design price in India starts within your Budget, Call +91 9671287099 to get exact quotation.
Join Our Happy customers network!






































 next to the Service Domain.
next to the Service Domain.